Natural farming is a chemical free traditional farming method in India.
Concept
Natural Farming is a chemical-free farming system rooted in Indian tradition enriched with modern understanding of ecology, resource recycling and on-farm resource optimization. It is considered as agroecology based diversified farming system which integrates crops, trees and livestock with functional biodiversity. It is largely based on on-farm biomass recycling with major stress on biomassmulching, use of on-farm cow dung-urine formulations; maintaining soil aeration and exclusion of all synthetic chemical inputs. Natural farming is expected to reduce dependency on purchased inputs. It is considered as a cost- effective farming practice with scope for increasing employment and rural development.

Scenario
Many states are already fallowing natural farming and have developed successful models. State of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh and Kerala are among the leading states. Currently, the acceptance and adoption of natural farming systems are at early stages and gradually gaining acceptance among the farming community.
Natural farming Practices
Natural farming aims at restoring soil health, maintenance of diversity, ensure animal welfare, stress on efficient use of natural/local resources and promote ecological fairness. Natural farming is an ecological farming approach where farming system
works with the natural biodiversity, encouraging the soil’s biological activity and managing the complexity of living organisms both plant and animal to thrive along with food production system.Important practices, essential for adoption of natural farming includes:
• No external inputs,
• Local seeds (use of local varieties), .
• On-farm produced microbial formulation for seed treatment (such as bijamrita),
• On-farm made microbial inoculants (Jivamrita) for soil enrichment,
• Cover crops and mulching with green and dry organic matter for nutrient recycling and for creating a suitable micro-climate for maximum beneficial microbial activity in soil.
• Mixed cropping,
• Managing diversity on farm through integration of trees
• Management of pests through diversity and local on-farm made botanical concoctions (such as neemastra, agniastra, neem ark, dashparni ark etc);
• Integration of livestock, especially of native breed for cow dung and cow urine as essential inputs for several practices and
• Water and moisture conservation.
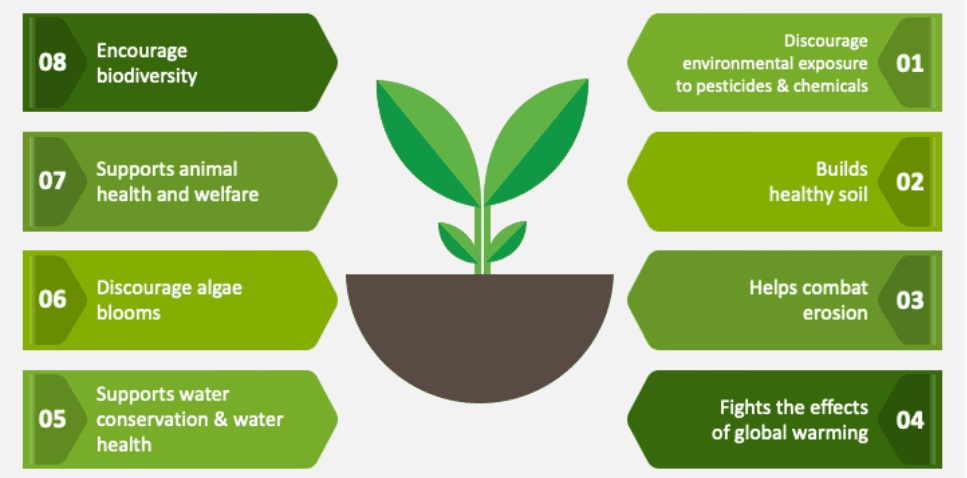
Aims and Objectives for Natural Farming promotion:
• Preserve natural flora and fauna
• Restore soil health and fertility and soil’s biological life
• Maintain diversity in crop production
• Efficient utilization of land and natural resources (light, air, water)
• Promote natural beneficial insects, animals and microbes in soil for nutrient recycling and biological control of pests and diseases
• Promotion of local breeds forlivestock integration
• Use of natural / local resource-based inputs
• Reduce input cost of agricultural production
• Improve economics of farmers






